cuda矩阵乘法优化
2025-02-25
cuda基本功,矩阵乘法优化。 在实际开发中,我们很少需要自己去写矩阵乘法,但是通过矩阵乘法的练习,是快速掌握cuda编程模型及其常用优化手段的最好方式。本文会首先介绍一下cuda编程的基本概念,然后写出一个基本的矩阵乘法kernel,在此基础上给出一个使用共享内存的优化版本。
1、cuda编程模型
gpu在快速发展过程中,cuda编程模型也在不断演化。cuda编程模型可以分为三部分,分别是线程模型、内存模型,以及执行模型。
1.1 线程模型
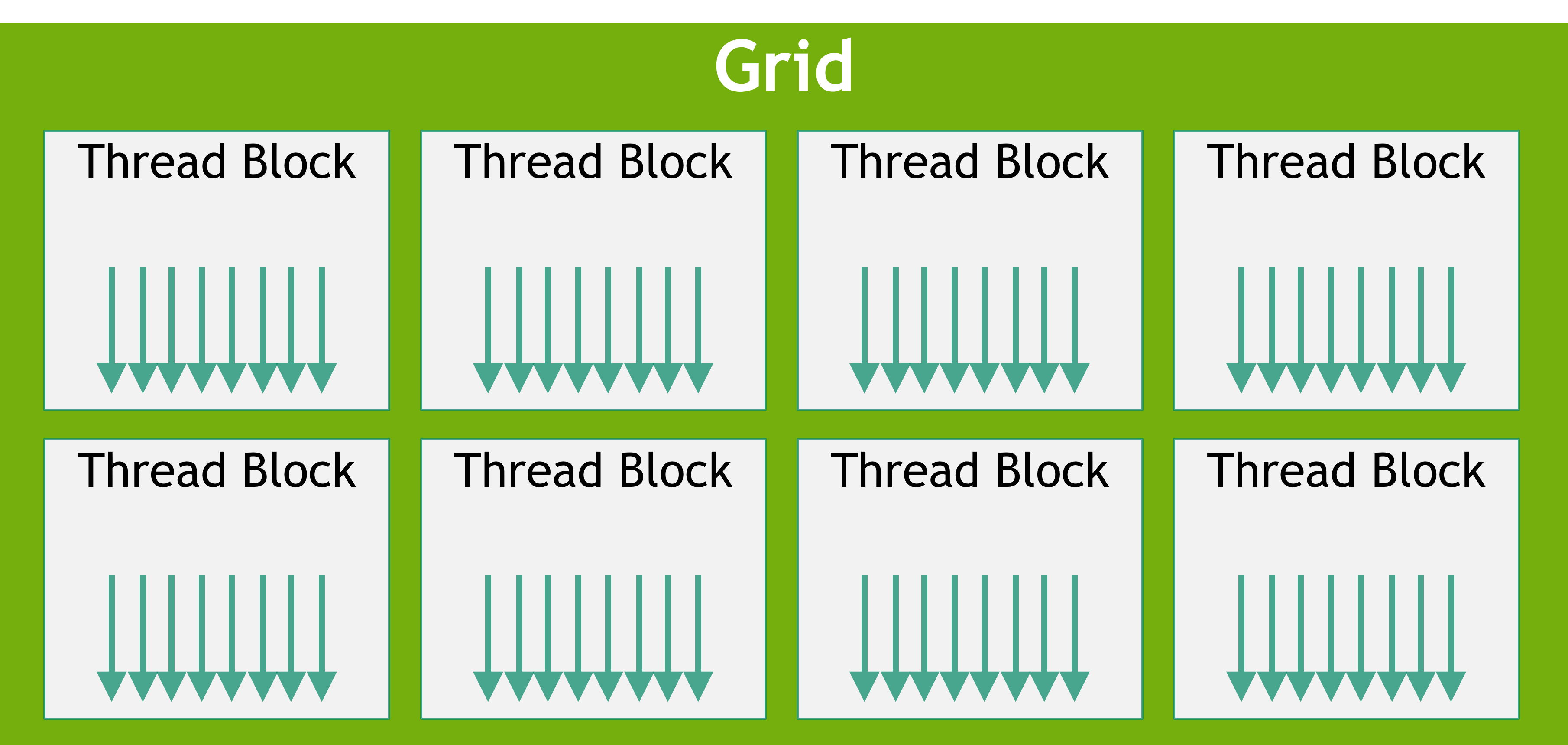
当你用cuda编程时,是以kernel为单位的,一个kernel就是一个使用cuda完成计算的函数。
当一个kernel被调用时,可以指定一组线程来执行这个kernel。这些线程被组织成上图所示的结构。可以看出来是一个两级的结构,grid和block。
这些编程模型是逻辑上的抽象,并不是物理上的抽象。说白了,就是一个给线程定位的方法。
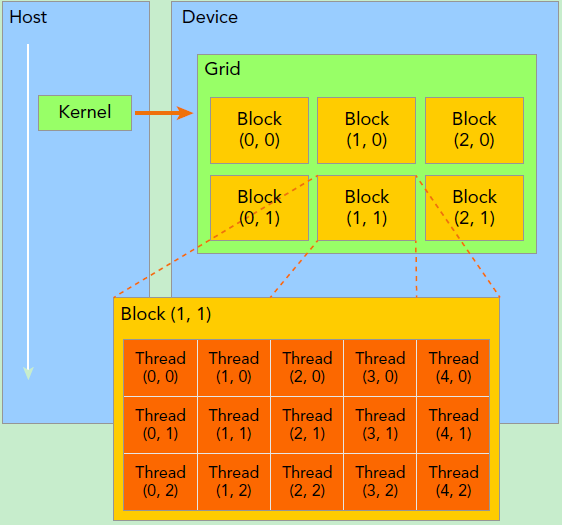
上图就展示了一个二维grid和二维block的结构。通过grid坐标和block坐标,我们可以唯一定位一个线程。 在实际编写kernel时,我们可以直接从kernel中获取当前线程的grid坐标和block坐标,具体的语法在后面会介绍。
1.2 内存模型
内存模型如下所示:
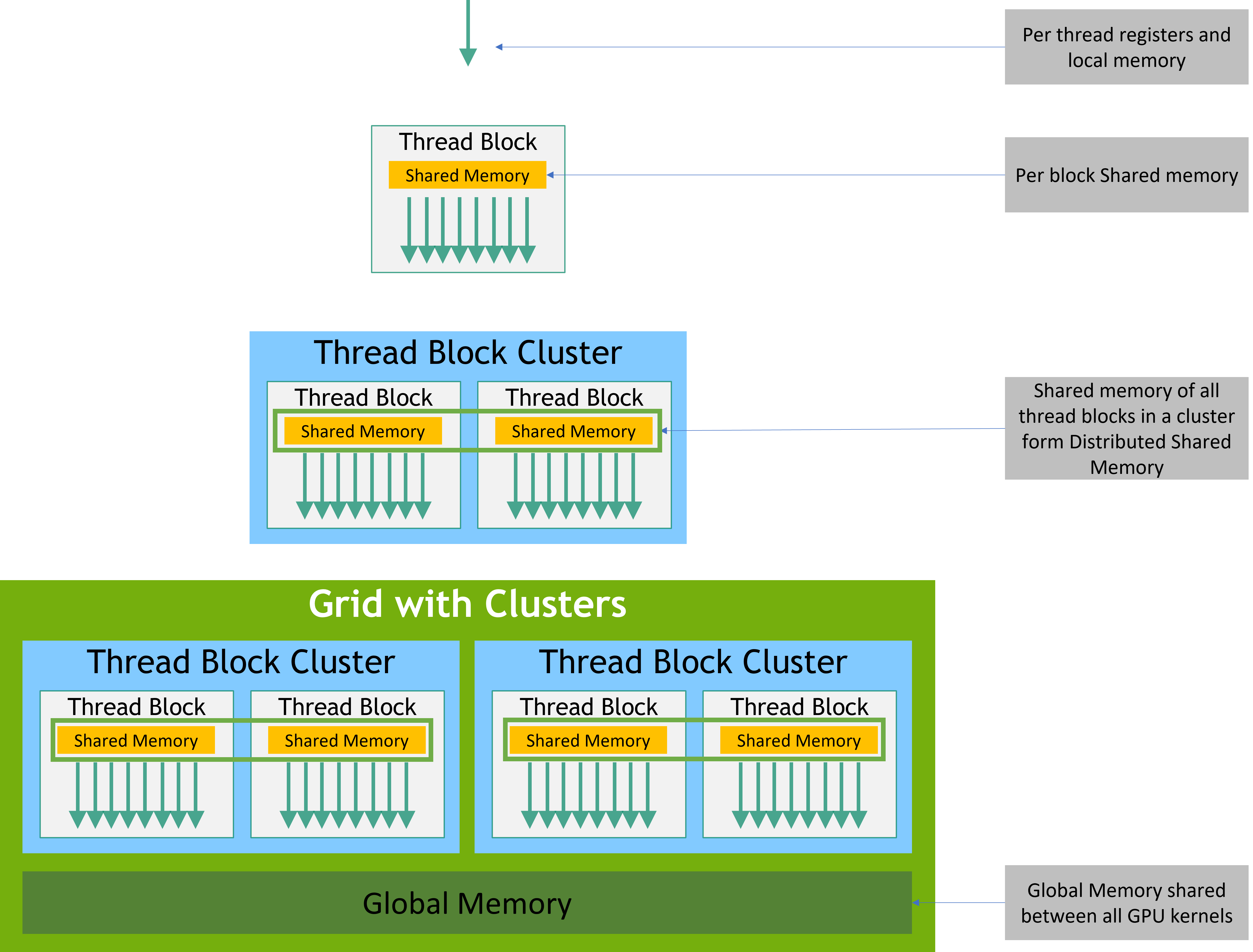
观察上图,可以看出两点:
1、内存是分级存储的,这么做自然是为了性能。从上到下的内存,存取速度越来越慢,但容量越来越大。
2、有个thread block cluster的抽象层次,这是在上节grid,block两级抽象中间加入的一个抽象层次,目的是让不同的block可以共享内存。仅在比较新的gpu上支持。
1.3 执行模型
cuda编写的kernel,在执行的时候是异构的。所谓异构,就是有的代码在cpu上执行,有的代码在gpu上执行。如下图所示:
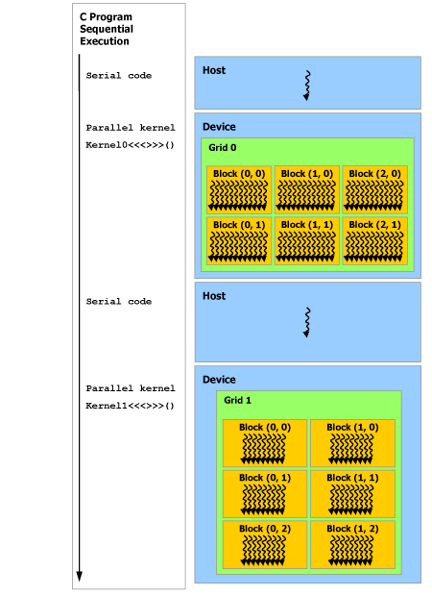
大概流程就是,首先将数据从内存搬到gpu显存上,然后从cpu上发起kernel调用,然后gpu开始执行kernel,执行完后,将结果从gpu显存搬回内存。
2、矩阵乘法
有了编程模型和内存模型和执行模型,我们就可以着手写矩阵乘法的kernel了。先看英伟达官方给的基础版本,然后就是英伟达官方给的优化版本。猛一接触,可能觉得有点难,有些没见过的关键字,不要慌,后面会详细介绍。
cuda编程的核心是实现计算资源、存储资源、数据三者之间的映射。
下面的矩阵乘法实现中,我们将为一个block分配一个子矩阵,这就是计算资源和数据之间的映射。
待会儿的优化版本中,我们进一步将子矩阵放到共享内存,这就是数据和存储资源之间的映射。
2.1 图示
矩阵乘法可以用下图表示:
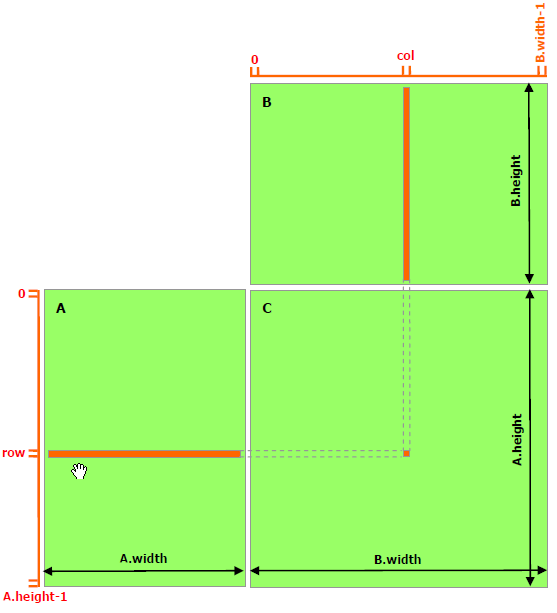
对于上面的图,大家应该不陌生,这里提示一下,请留意结果矩阵的宽高和相乘矩阵的宽高之间的关系。
2.2 基本版本
// Matrices are stored in row-major order:
// M(row, col) = *(M.elements + row * M.width + col)
typedef struct {
int width;
int height;
float* elements;
} Matrix;
// Thread block size
#define BLOCK_SIZE 16
// Forward declaration of the matrix multiplication kernel
__global__ void MatMulKernel(const Matrix, const Matrix, Matrix);
// Matrix multiplication - Host code
// Matrix dimensions are assumed to be multiples of BLOCK_SIZE
void MatMul(const Matrix A, const Matrix B, Matrix C)
{
// Load A and B to device memory
Matrix d_A;
d_A.width = A.width; d_A.height = A.height;
size_t size = A.width * A.height * sizeof(float);
cudaMalloc(&d_A.elements, size);
cudaMemcpy(d_A.elements, A.elements, size,
cudaMemcpyHostToDevice);
Matrix d_B;
d_B.width = B.width; d_B.height = B.height;
size = B.width * B.height * sizeof(float);
cudaMalloc(&d_B.elements, size);
cudaMemcpy(d_B.elements, B.elements, size,
cudaMemcpyHostToDevice);
// Allocate C in device memory
Matrix d_C;
d_C.width = C.width; d_C.height = C.height;
size = C.width * C.height * sizeof(float);
cudaMalloc(&d_C.elements, size);
// Invoke kernel
dim3 dimBlock(BLOCK_SIZE, BLOCK_SIZE);
dim3 dimGrid(B.width / dimBlock.x, A.height / dimBlock.y);
MatMulKernel<<<dimGrid, dimBlock>>>(d_A, d_B, d_C);
// Read C from device memory
cudaMemcpy(C.elements, d_C.elements, size,
cudaMemcpyDeviceToHost);
// Free device memory
cudaFree(d_A.elements);
cudaFree(d_B.elements);
cudaFree(d_C.elements);
}
// Matrix multiplication kernel called by MatMul()
__global__ void MatMulKernel(Matrix A, Matrix B, Matrix C)
{
// Each thread computes one element of C
// by accumulating results into Cvalue
float Cvalue = 0;
int row = blockIdx.y * blockDim.y + threadIdx.y;
int col = blockIdx.x * blockDim.x + threadIdx.x;
for (int e = 0; e < A.width; ++e)
Cvalue += A.elements[row * A.width + e]
* B.elements[e * B.width + col];
C.elements[row * C.width + col] = Cvalue;
}
上面的代码中, __global__关键字表示是可以从cpu上调用的kernel。
blockIdx 表示当前线程所在的block的坐标。
threadIdx 表示当前线程的坐标。
blockDim 表示一个block的维度。
2.3 优化版本
矩阵乘法中,A的每一行都将与B的每一列相乘,在上面的实现中,不管是A中的行,还是B中的列,都被多次从全局内存中读取。这个速度是很慢的。 我们可以将A和B进行分块,然后利用共享内存,将A和B的子块加载到共享内存中,然后计算得到结果矩阵的子块。如下图所示:
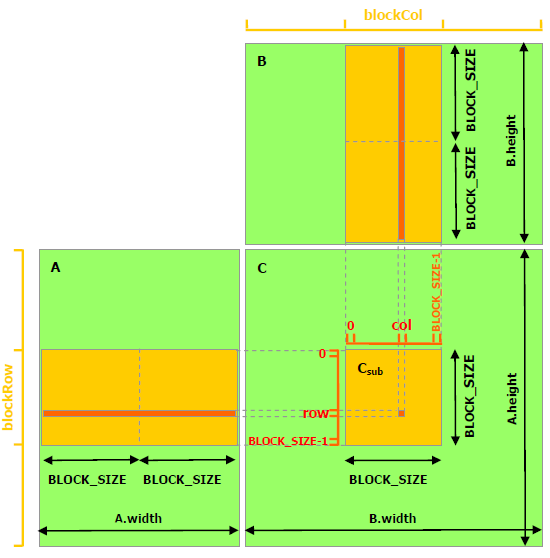
// Matrices are stored in row-major order:
// M(row, col) = *(M.elements + row * M.stride + col)
typedef struct {
int width;
int height;
int stride;
float* elements;
} Matrix;
// Get a matrix element
__device__ float GetElement(const Matrix A, int row, int col)
{
return A.elements[row * A.stride + col];
}
// Set a matrix element
__device__ void SetElement(Matrix A, int row, int col,
float value)
{
A.elements[row * A.stride + col] = value;
}
// Get the BLOCK_SIZExBLOCK_SIZE sub-matrix Asub of A that is
// located col sub-matrices to the right and row sub-matrices down
// from the upper-left corner of A
__device__ Matrix GetSubMatrix(Matrix A, int row, int col)
{
Matrix Asub;
Asub.width = BLOCK_SIZE;
Asub.height = BLOCK_SIZE;
Asub.stride = A.stride;
Asub.elements = &A.elements[A.stride * BLOCK_SIZE * row
+ BLOCK_SIZE * col];
return Asub;
}
// Thread block size
#define BLOCK_SIZE 16
// Forward declaration of the matrix multiplication kernel
__global__ void MatMulKernel(const Matrix, const Matrix, Matrix);
// Matrix multiplication - Host code
// Matrix dimensions are assumed to be multiples of BLOCK_SIZE
void MatMul(const Matrix A, const Matrix B, Matrix C)
{
// Load A and B to device memory
Matrix d_A;
d_A.width = d_A.stride = A.width; d_A.height = A.height;
size_t size = A.width * A.height * sizeof(float);
cudaMalloc(&d_A.elements, size);
cudaMemcpy(d_A.elements, A.elements, size,
cudaMemcpyHostToDevice);
Matrix d_B;
d_B.width = d_B.stride = B.width; d_B.height = B.height;
size = B.width * B.height * sizeof(float);
cudaMalloc(&d_B.elements, size);
cudaMemcpy(d_B.elements, B.elements, size,
cudaMemcpyHostToDevice);
// Allocate C in device memory
Matrix d_C;
d_C.width = d_C.stride = C.width; d_C.height = C.height;
size = C.width * C.height * sizeof(float);
cudaMalloc(&d_C.elements, size);
// Invoke kernel
dim3 dimBlock(BLOCK_SIZE, BLOCK_SIZE);
dim3 dimGrid(B.width / dimBlock.x, A.height / dimBlock.y);
MatMulKernel<<<dimGrid, dimBlock>>>(d_A, d_B, d_C);
// Read C from device memory
cudaMemcpy(C.elements, d_C.elements, size,
cudaMemcpyDeviceToHost);
// Free device memory
cudaFree(d_A.elements);
cudaFree(d_B.elements);
cudaFree(d_C.elements);
}
// Matrix multiplication kernel called by MatMul()
__global__ void MatMulKernel(Matrix A, Matrix B, Matrix C)
{
// Block row and column
int blockRow = blockIdx.y;
int blockCol = blockIdx.x;
// Each thread block computes one sub-matrix Csub of C
Matrix Csub = GetSubMatrix(C, blockRow, blockCol);
// Each thread computes one element of Csub
// by accumulating results into Cvalue
float Cvalue = 0;
// Thread row and column within Csub
int row = threadIdx.y;
int col = threadIdx.x;
// Loop over all the sub-matrices of A and B that are
// required to compute Csub
// Multiply each pair of sub-matrices together
// and accumulate the results
for (int m = 0; m < (A.width / BLOCK_SIZE); ++m) {
// Get sub-matrix Asub of A
Matrix Asub = GetSubMatrix(A, blockRow, m);
// Get sub-matrix Bsub of B
Matrix Bsub = GetSubMatrix(B, m, blockCol);
// Shared memory used to store Asub and Bsub respectively
__shared__ float As[BLOCK_SIZE][BLOCK_SIZE];
__shared__ float Bs[BLOCK_SIZE][BLOCK_SIZE];
// Load Asub and Bsub from device memory to shared memory
// Each thread loads one element of each sub-matrix
As[row][col] = GetElement(Asub, row, col);
Bs[row][col] = GetElement(Bsub, row, col);
// Synchronize to make sure the sub-matrices are loaded
// before starting the computation
__syncthreads();
// Multiply Asub and Bsub together
for (int e = 0; e < BLOCK_SIZE; ++e)
Cvalue += As[row][e] * Bs[e][col];
// Synchronize to make sure that the preceding
// computation is done before loading two new
// sub-matrices of A and B in the next iteration
__syncthreads();
}
// Write Csub to device memory
// Each thread writes one element
SetElement(Csub, row, col, Cvalue);
}
2.4 矩阵尺寸不满足BLOCK_SIZE整除
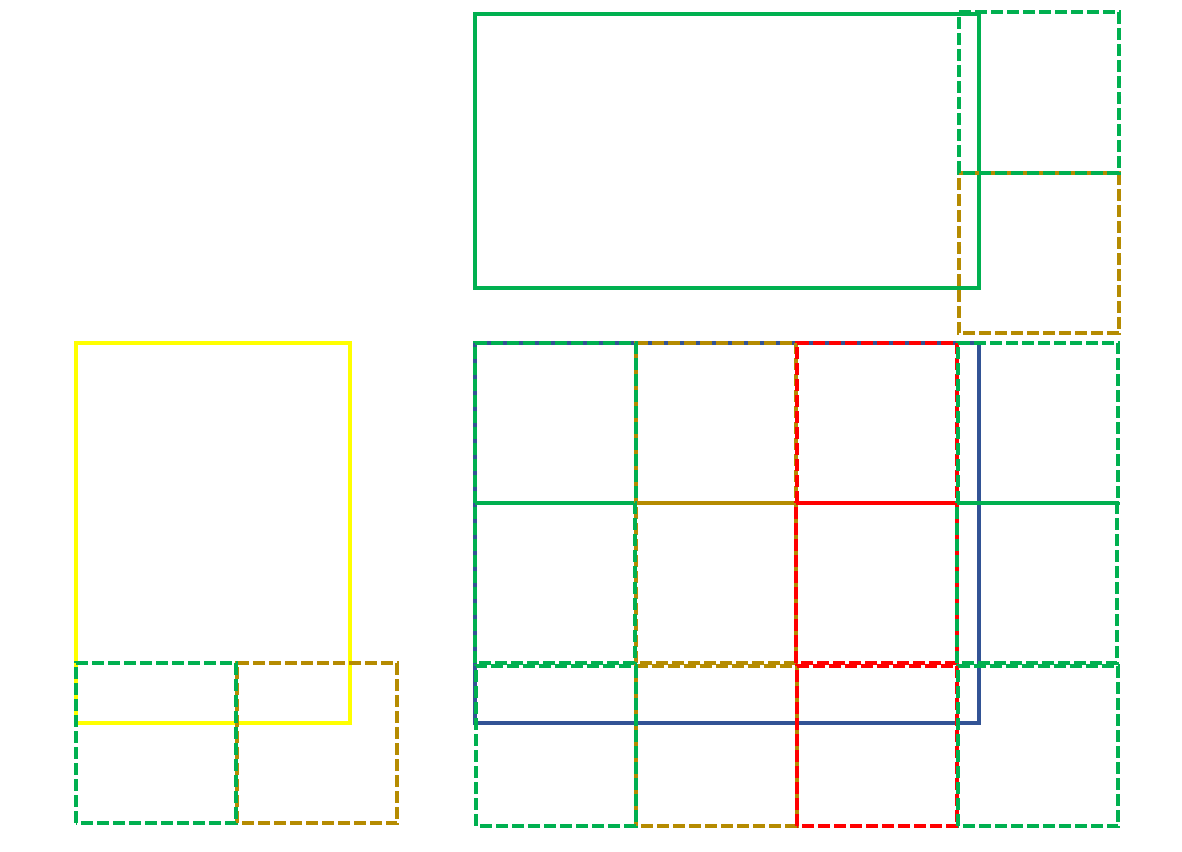
如上图所示,我们重点观察C矩阵右下角的block,思考在这种情况下,上面的代码应该如何修改?
当我们设计cuda kernel时,我觉得时刻让大脑处在合适的抽象层次,是确保思路清晰的关键。
比如在矩阵乘法中,我们首先定义好block的size,比如16*16,然后想想用这个block铺在结果矩阵上。
如上图右下角所示。
这一步,我们实际上是在为线程分配计算任务。每个block的任务就是它覆盖的C矩阵的部分。
然后,我们开始关注单个block的计算,为了突出一般性,我们关注最右下角的block。
当我们关注这个block的计算时。我们开始从block内部的线程角度思考问题。
这里需要花点时间多琢磨一下,虽然你在从一个线程的角度考虑问题。
但因为使用共享内存,你还要想着整个block的线程之间的协作。这里特指填充As和Bs。
// Matrices are stored in row-major order:
// M(row, col) = *(M.elements + row * M.stride + col)
typedef struct {
int width;
int height;
int stride;
float* elements;
} Matrix;
// Get a matrix element
__device__ float GetElement(const Matrix A, int row, int col)
{
return A.elements[row * A.stride + col];
}
// Set a matrix element
__device__ void SetElement(Matrix A, int row, int col,
float value)
{
A.elements[row * A.stride + col] = value;
}
// Get the BLOCK_SIZExBLOCK_SIZE sub-matrix Asub of A that is
// located col sub-matrices to the right and row sub-matrices down
// from the upper-left corner of A
// 这里需要留心的一点,就是子矩阵Asub和A的stride一样。
__device__ Matrix GetSubMatrix(Matrix A, int row, int col)
{
Matrix Asub;
Asub.width = BLOCK_SIZE;
Asub.height = BLOCK_SIZE;
Asub.stride = A.stride;
Asub.elements = &A.elements[A.stride * BLOCK_SIZE * row
+ BLOCK_SIZE * col];
return Asub;
}
// Thread block size
#define BLOCK_SIZE 16
// Forward declaration of the matrix multiplication kernel
__global__ void MatMulKernel(const Matrix, const Matrix, Matrix);
// Matrix multiplication - Host code
// Matrix dimensions are assumed to be multiples of BLOCK_SIZE
void MatMul(const Matrix A, const Matrix B, Matrix C)
{
// Load A and B to device memory
Matrix d_A;
d_A.width = d_A.stride = A.width; d_A.height = A.height;
size_t size = A.width * A.height * sizeof(float);
cudaMalloc(&d_A.elements, size);
cudaMemcpy(d_A.elements, A.elements, size,
cudaMemcpyHostToDevice);
Matrix d_B;
d_B.width = d_B.stride = B.width; d_B.height = B.height;
size = B.width * B.height * sizeof(float);
cudaMalloc(&d_B.elements, size);
cudaMemcpy(d_B.elements, B.elements, size,
cudaMemcpyHostToDevice);
// Allocate C in device memory
Matrix d_C;
d_C.width = d_C.stride = C.width; d_C.height = C.height;
size = C.width * C.height * sizeof(float);
cudaMalloc(&d_C.elements, size);
// Invoke kernel
dim3 dimBlock(BLOCK_SIZE, BLOCK_SIZE);
dim3 dimGrid((B.width + dimBlock.x - 1) / dimBlock.x, (A.height + dimBlock.y - 1) / dimBlock.y);
MatMulKernel<<<dimGrid, dimBlock>>>(d_A, d_B, d_C);
// Read C from device memory
cudaMemcpy(C.elements, d_C.elements, size,
cudaMemcpyDeviceToHost);
// Free device memory
cudaFree(d_A.elements);
cudaFree(d_B.elements);
cudaFree(d_C.elements);
}
// Matrix multiplication kernel called by MatMul()
__global__ void MatMulKernel(Matrix A, Matrix B, Matrix C)
{
// Block row and column
int blockRow = blockIdx.y;
int blockCol = blockIdx.x;
// Thread row and column within Csub
int row = threadIdx.y;
int col = threadIdx.x;
// 计算全局索引
int global_row = blockRow * BLOCK_SIZE + row;
int global_col = blockCol * BLOCK_SIZE + col;
// Each thread block computes one sub-matrix Csub of C
Matrix Csub = GetSubMatrix(C, blockRow, blockCol);
// Each thread computes one element of Csub
// by accumulating results into Cvalue
float Cvalue = 0;
// Loop over all the sub-matrices of A and B that are
// required to compute Csub
// Multiply each pair of sub-matrices together
// and accumulate the results
for (int m = 0; m < ((A.width + BLOCK_SIZE - 1) / BLOCK_SIZE); ++m) {
// Get sub-matrix Asub of A
Matrix Asub = GetSubMatrix(A, blockRow, m);
// Get sub-matrix Bsub of B
Matrix Bsub = GetSubMatrix(B, m, blockCol);
// Shared memory used to store Asub and Bsub respectively
__shared__ float As[BLOCK_SIZE][BLOCK_SIZE];
__shared__ float Bs[BLOCK_SIZE][BLOCK_SIZE];
// Load Asub and Bsub from device memory to shared memory
// Each thread loads one element of each sub-matrix
// 检查是否在矩阵范围内
if (global_row < A.height && (m * BLOCK_SIZE + col) < A.width) {
As[row][col] = GetElement(Asub, row, col);
} else {
As[row][col] = 0;
}
if ((m * BLOCK_SIZE + row) < B.height && global_col < B.width) {
Bs[row][col] = GetElement(Bsub, row, col);
} else {
Bs[row][col] = 0;
}
// Synchronize to make sure the sub-matrices are loaded
// before starting the computation
__syncthreads();
// Multiply Asub and Bsub together
for (int e = 0; e < BLOCK_SIZE; ++e)
Cvalue += As[row][e] * Bs[e][col];
// Synchronize to make sure that the preceding
// computation is done before loading two new
// sub-matrices of A and B in the next iteration
__syncthreads();
}
// Write Csub to device memory
// Each thread writes one element
// 检查是否在矩阵范围内
if (global_row < C.height && global_col < C.width) {
SetElement(Csub, row, col, Cvalue);
}
}
主要的修改点:
1、grid的维度计算考虑了矩阵尺寸不满足BLOCK_SIZE整除的情况
2、tile循环考虑了矩阵尺寸不满足BLOCK_SIZE整除的情况
3、初始化As和Bs时,考虑了矩阵范围外的元素
4、写入Csub时,考虑了矩阵范围外的元素
Reference:
原创文章,转载请注明出处,否则拒绝转载!
本文链接:抬头看浏览器地址栏
最新文章
- 2025年文章总结 2025-12-29
- Flux-Text执行流程记录 2025-07-14
- livetalking数字人执行流程 2025-07-13
- Step1X-Edit执行流程(二) 2025-06-25
- Step1X-Edit执行流程(一) 2025-06-24
- 女儿突然知道关心人了 2025-04-28
- shfl_xor_sync原语 2025-04-22
- MHA, GQA, MQA, MLA的代码 2025-04-01
- Bank Conflicts简介 2025-03-05
- FlashAttention解读 2025-03-01